- NITRIC OXIDE "THE MOLECULE OF LIFE"

If you would like to Download Free, Dr Q’s “TOP 10 HEALTH BENEFITS OF NITRIC OXIDE”, simply fill out the form and press submit!
- Protect and Restore Your Body
- CRITICAL FINDINGS
NITRIC OXIDE - FROM MENACE TO MARVEL OF THE DECADE

REPRODUCTIVE AND CARDIOVASCULAR RESEARCH GROUP
NITRIC OXIDE - FROM MENACE TO MARVEL OF THE DECADE

THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF ERECTION

SPIRELING HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE LINKED TO NO DEFICIENCY
NITRIC OXIDE (NO) PREVENTS BLOOD VESSEL INFLAMATION
LINKS BULD OF SPORADIC AND FAMILIAL PARKINSON'S DISEASE

UC IRVIE RESEARCHERS REVEAL STRUCTURE OF MOLECULE THAT REGULATE BLOOD PRESSURE
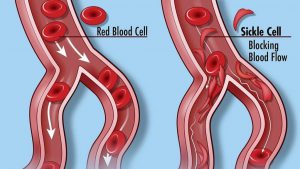
STUDY POINTS - ROLE OF NO WITH SICKLE CELL ANEMIA
KEY TO BOOTING UP

NO DEFICIENCY RAISES CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE RISK IN AFRICAN AMERICANS
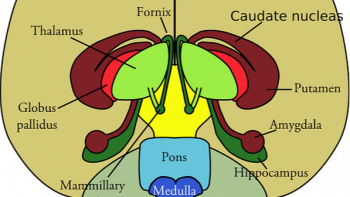
CORTISOL FEED BACK TO THE THALAMUS IS SELECTIVELY ENHANCED BY NO
- WHAT IS NITRIC OXIDE?
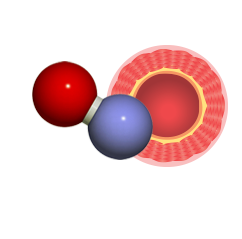
Nitric oxide helps maintain, repair and defend every cell in the human body. One part nitrogen, one part oxygen, this simple molecule is deeply embedded in nearly every major aspect of human physiology.
…While nitric oxide is produced in the human body, most people don’t make enough nitric oxide to maintain optimal health….
To date, more than 70,000 scientific papers have been published regarding some aspect of nitric oxide’s beneficial role in human health and wellness. Valuable in combating pain, inflammation, digestive problems, insomnia, diabetes and injury, nitric oxide is also consistently linked to increased energy, improved sexual function and even weight loss.
While nitric oxide is produced in the human body, most people don’t make enough nitric oxide to maintain optimal health. The Morinda citrifolia (noni) plant offers a solution. Rich in the components necessary to create the miracle molecule, it is no wonder the people of the islands have used the noni plant to cure various afflictions for centuries.
NITRIC OXIDE HISTORY
Since three scientists won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1998 for discovering nitric oxide’s role in cell signaling, nitric oxide has become one of the most researched molecules and medical topics in recent history. However, our understanding of this tiny “miracle molecule” has grown from humble beginnings.

DISCOVERY
First studied in 1772 by Joseph Priestly, who called it “nitrous air,” nitric oxide was first discovered as a colorless, toxic gas. Unfortunately, the classification of toxid gas and air pollutant continued to be the only labels nitric oxide was afforded until 1987, when it was shown to actually be produced naturally in the body.

NONI FROM THE ISLANDS
Scientists have only recently discovered the link between nitric oxide and the noni plant (Morinda citrifolia). Noni originally came from Polynesia, Micronesia and the Hawaiian islands. The Polynesian people have been using noni for thousands of years as a cure-all plant.

THE NONI PLANT (MORINDA CITRIFOIA)
During the 1990’s, purchase and distribution of noni started to grow exponentially around the world. Scientists started to notice a correlation between the patients using the noni plant and having nitric oxide in the body.
From 1999 to 2000, Dr. Thomas Burke and other researches at Integrated Systems Physiology conducted research, which found that noni fruit juice created nitric oxide in the body. We now know extracts from the entire noni plant generate additional nitric oxide in the body, providing noni with its numerous healing powers.
THE NITROGLYCERIN ERA
THE MOLECULE OF LIFE
By the early 1980’s, scientists had conclusively proven that nitric oxide occurred naturally within the human body. By 1987, nitric oxide’s role in regulation blood pressure and relieving heart conditions was well-established. Two years later, research revealed that nitric oxide is used by macrophages to kill tumor cells and bacteria.
In 1992, nitric oxide was voted “Molecule of the Year” by Science magazine. The importance of nitric oxide became front page news in 1998 when Louis J. Ignerro, Robert F. Furchgott and Ferid Murad were awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine and Physiology. These scientists identified nitric oxide as a signaling molecule, opening up a new way of treatment for millions of patients.
Now, in 2006, more than 70,000 scientific papers have been published on nitric oxide and its seemingly endless role in health and physiology.
- NITRIC OXIDE
Nitric Oxide is actually a highly reactive gas that is produced naturally within the body. It has only a short life of a few seconds. But within its miniscule lifespan, nitric oxide plays the role of the human body’s most important “messenger.”
Nitric oxide improves the blood flow to the tissue, allowing more oxygen, nutrients, vitamins, and growth factors to be delivered to every cell of the body.
As part of its role, nitric oxide is involved in several physiological functions including blood circulation, nerve communication, learning, memory, digestion and fighting disease.
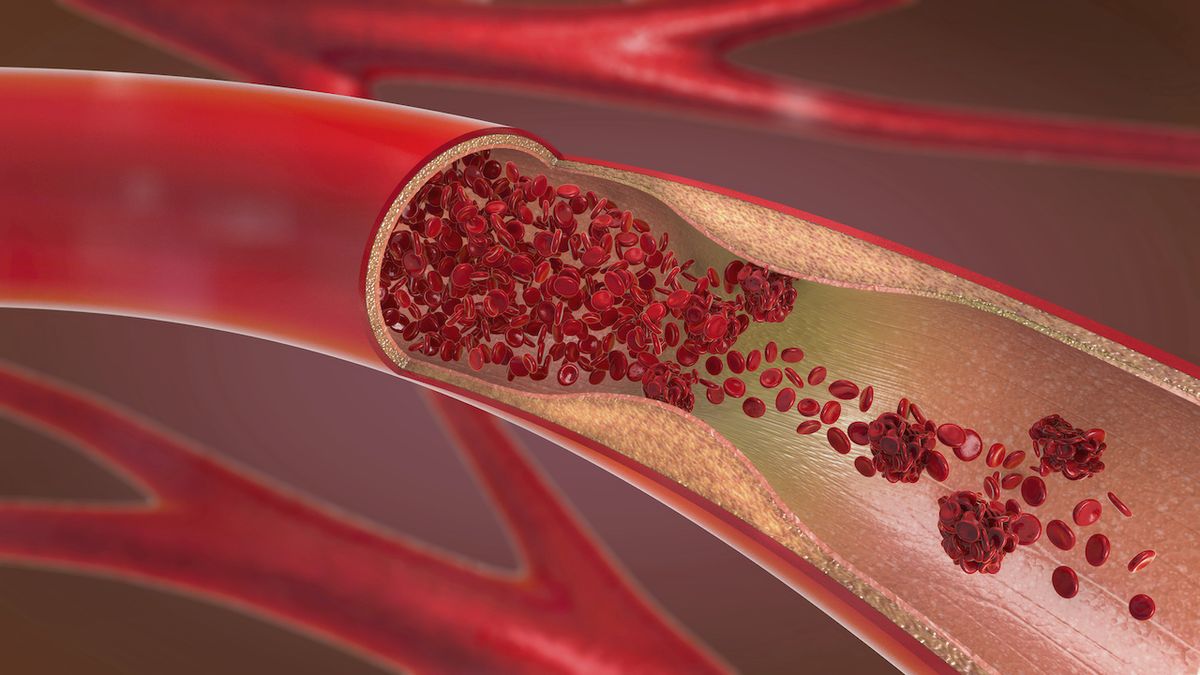
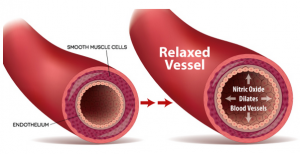
BLOOD CIRCULATION (HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE)
One of nitric oxide’s best known functions is as a regulator of blood pressure. In a process referred to as vasodilation, nitric oxide relaxes and widens blood vessels, which improves blood flow and prevents clotting. Nitric oxide accomplishes this by spreading from the innermost cell layer of the arteries to their underlying muscle cells. Nitric oxide prevents these cells from contracting, leaving them relaxed and dilated. Through the extracts of the noni tree, nitric oxide can be a useful adjunct to help millions of people in normalizing their blood pressure along with a healthy diet and exercise.

NITRIC OXIDE HELPS REDUCE PAIN
Nitric oxide helps reduce pain, when many drugs are being prescribed for pain relief. Scientific research shows that the pain-relieving effects of medications like morphine, aspirin, and oxycontin are due to the release of nitric oxide.

NITRIC OXIDE HELPS WITH WEIGHT LOSS
Inside the cells of the body are tiny mitochondria, the places where food and oxygen are turned into energy. The mitochondria is where all fat is burned, in addition to generating almost all of a persons energy used and controlling cellular metabolism. Research is showing that nitric oxide not only stimulates the creation of new mitochondria, but also may make each individual mitochondrion larger, which helps burn even more fat and therefore could result in weight loss.

NITRIC OXIDE INCREASES ENERGY
Exercise increases nitric oxide and taking a substance that increases nitric oxide increases the energy to exercise.
NITRIC OXIDE REDUCES INFLAMMATION
Nitric oxide inhibits inflammation in blood vessels by blocking the inflammation that occurs in damaged endothelial cells. If these cells become damaged or dysfunctional, nitric oxide production becomes impaired, which leads to more inflammation and tissue damage.

NITRIC OXIDE IMPROVES DIGESTION
Nitric oxide is heavily involved in the processes of the digestive tract. Nitric oxide regulates blood flow to the gut, which helps you digest food and keeps the lining of the gut undamaged to protect from invaders. It also actively is able to kill off those invaders.

NITRIC OXIDE AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
Nitric oxide acts as a powerful weapon against infections. It acts as a signaling molecule between immune cells.

NITRIC OXIDE AND THE PREVENTION OF CANCER
Nitric oxide acts as a powerful weapon against infections. It acts as a signaling molecule between immune cells.
NITRIC OXIDE HELPING THE BRAIN
Nitric oxide is distributed throughout the brain and may have an involvement in almost all of its normal physiological functions. A cell in the brain is responsible for releasing a chemical messenger called glutamate, which stimulates another cell, a receptor cell, with this chemical to release nitric oxide. If it is strongly stimulated, the receptor sends back a nitric oxide molecule to tell the sender that the message was received, and asks it to send an even stronger message next time.
what Our client’s say
